Chemical Peeling Advantages And Disadvantages
Chemical peeling is a skincare treatment where specific acids or chemicals are applied to the skin to exfoliate and remove its outer layers. This process helps to rejuvenate the skin by promoting the shedding of damaged or dead cells, revealing a smoother, more even-toned layer underneath. The peeling effect can vary from mild exfoliation to deeper treatment, depending on the type and strength of the chemical used.
Mechanism of Chemical Peeling
- Dissolution of Keratin Layer: Chemical peeling agents, typically acids like glycolic acid or salicylic acid, work by dissolving the keratin layer on the skin’s surface. This keratin layer consists of dead skin cells that can make the skin appear dull and rough.
- Inflammatory Reaction: As the acid penetrates the skin, it causes a controlled, mild inflammatory reaction. This inflammation is a signal to the skin to begin the healing process, which includes increased production of new skin cells.
- Skin Regeneration and Texture Improvement: The peeling process encourages the turnover of skin cells, leading to the shedding of old, damaged layers and the formation of new, healthier skin. Over time, this results in improved skin texture, a more even skin tone, and the repair of the keratin layer, leaving the skin smoother and more radiant.
Treatment Expectations
- Multiple Sessions Required: Achieving noticeable results with chemical peeling typically requires multiple sessions. The full benefits become apparent over time as the skin undergoes repeated exfoliation and regeneration.
- Individual Variation: The effectiveness of chemical peeling varies depending on individual factors such as skin condition, age, and overall skin health. Personalized treatment plans are often necessary to address specific concerns.
- Treatment Schedule: For acne, sessions might be scheduled every two weeks to address ongoing breakouts and prevent future issues. For hyperpigmentation or dark spots, a longer-term treatment plan may be needed, with sessions spaced out over several months to achieve optimal results.
Benefits and Effects

- Acne:
- Improvement: Chemical peeling can help improve acne by clearing clogged pores and reducing excess oil production. This can lead to fewer breakouts and a clearer complexion.
- Variability: Its effectiveness can vary based on the type of acne and individual skin response. It may not be suitable for everyone and often needs to be combined with other treatments for best results.
- Acne Scars: There is limited evidence supporting its effectiveness on acne scars. Other treatments might be more appropriate for addressing post-acne scarring.
- Small Spots:
- Sun Damage: Chemical peels can improve small spots caused by sun exposure, such as age spots or sun spots, by promoting cell turnover and revealing fresher skin underneath.
- Limitations: They are generally not effective for genetic conditions like freckles or melasma, which require different approaches for treatment.
- Fine Wrinkles:
- Improvement: By stimulating skin regeneration and increasing cell turnover, chemical peels can help improve the appearance of fine wrinkles and give the skin a smoother texture.
- Limitations: They are less effective for deep wrinkles and more advanced signs of aging, which may need more intensive treatments like laser therapy or injectable fillers.
Risks and Side Effects
- Skin Sensitivity:
- Increased Vulnerability: After a chemical peel, the removal of the protective keratin layer makes the skin more sensitive to UV rays. This increased sensitivity requires careful protection and post-treatment care.
- Common Side Effects:
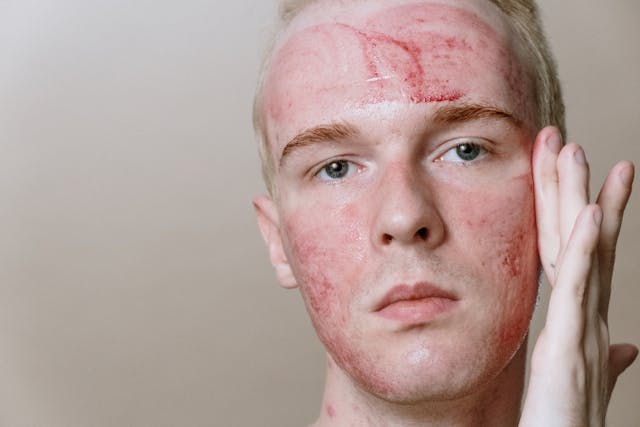
- Redness: Skin may appear red and inflamed immediately after the treatment, similar to a sunburn.
- Pigmentation Changes: There can be temporary or permanent changes in skin pigmentation, including darkening or lightening of the treated areas.
- Dryness: The skin may become excessively dry and flaky as it heals.
- Potential Scarring: There is a risk of scarring, including keloids, particularly for individuals prone to such reactions or those with darker skin tones.
Types of Peeling Agents

- AHA (Alpha Hydroxy Acid):
- Source: Typically derived from fruits and milk, such as glycolic acid (from sugar cane) and lactic acid (from milk).
- Function: Promotes cell turnover by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, revealing fresher skin underneath.
- Suitability: Generally safe for most skin types, including sensitive skin. Mild and effective for improving skin texture, reducing fine lines, and brightening the complexion.
- BHA (Beta Hydroxy Acid):
- Source: Most commonly salicylic acid, derived from willow bark.
- Function: Penetrates deeper into pores to exfoliate inside the follicle, making it effective for oily and acne-prone skin.
- Suitability: Ideal for treating acne and blackheads, but may not be as suitable for very sensitive skin.
- TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid):
- Source: A synthetic acid used in various strengths.
- Function: Works on the outer and middle layers of skin to treat deeper skin issues such as more pronounced wrinkles and significant hyperpigmentation.
- Suitability: Requires careful use and professional application due to its potency. Suitable for more severe skin concerns.
- Phenol:
- Source: A strong, synthetic acid.
- Function: Provides deep peeling by affecting the deeper layers of the skin, used for severe skin issues and deep wrinkles.
- Suitability: Most intense and invasive type of chemical peel, often requiring longer recovery time and professional supervision. Generally avoided for sensitive skin types, including Japanese skin, due to potential risks.
Contraindications
Ongoing Medical Conditions:Chemical peels can exacerbate these conditions or cause additional irritation.
Examples: Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or severe rosacea.
Pregnancy:Certain chemical peels and their ingredients may not be safe during pregnancy. It’s best to avoid treatments and consult a healthcare provider.
Keloid-Prone Skin:Individuals prone to keloid scarring should avoid chemical peels as they may increase the risk of abnormal scarring.
Certain Medications:These medications can heighten the risk of adverse reactions or complications from chemical peels.
Examples: Medications that increase skin sensitivity or affect skin healing, such as oral retinoids or anticoagulants.












4 comments