How To Identify And Treat Different Types Of Acne
Navigating the world of acne can be challenging. This article breaks down the different types of acne—whiteheads, blackheads, inflammatory acne, and pustular acne—exploring their unique characteristics and risks. We’ll discuss effective treatments, from basic skincare routines to advanced dermatological options, to help you manage and reduce acne. Understanding each type and applying targeted solutions can make a significant difference in achieving clear, healthy skin and preventing long-term scarring. Dive in to find out how to tackle acne effectively.
Whiteheads
Identification: Whiteheads are small, raised, colorless pimples that form when sebum (skin oil) gets trapped in clogged pores. They are not typically inflamed, painful, or red. It’s important not to touch or squeeze whiteheads, as this can lead to inflammation or potential scarring.
Treatment:
- Regular Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser to keep your skin clean and reduce the risk of clogged pores.
- Balanced Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to manage sebum production and minimize whiteheads.
- Chemical Peels and Iontophoresis: These treatments can accelerate the improvement of whiteheads by exfoliating the skin and promoting deeper cleansing.
Blackheads
Identification: Blackheads are essentially oxidized whiteheads. They appear darker due to exposure to air, which causes the sebum in the clogged pore to oxidize. Like whiteheads, blackheads don’t cause inflammation or pain, but they can be managed effectively with early intervention.
Treatment:
- Avoid Aggressive Products: Steer clear of harsh pore-cleansing products that may irritate the skin or worsen blackheads.
- Regular Exfoliation: Use products with exfoliating ingredients like salicylic acid to help keep pores clear and prevent blackheads from forming.
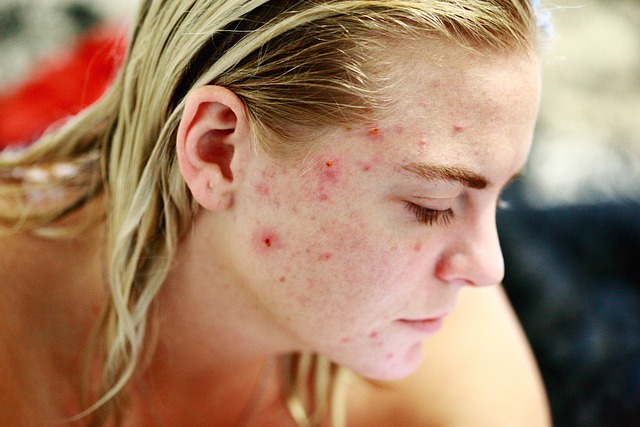
Inflammatory Acne
Identification:
- Characteristics: Inflammatory acne is marked by redness, pain, and itching. This type of acne is often caused by bacterial infections, primarily from acne bacteria.
- Risks: As inflammation increases, so does the risk of scarring, making it essential to manage this type of acne carefully.
Treatment:
- Medications: Use treatments focused on reducing inflammation, such as topical or oral medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
- Avoid Irritation: Refrain from scratching or applying makeup to the affected areas, as this can exacerbate irritation.
- Dermatological Advice: Consult a dermatologist for personalized treatment plans to effectively manage inflammatory acne and minimize scarring.
Pustular Acne
Identification:
- Characteristics: Pustular acne is a more severe form of inflammatory acne characterized by the presence of pus-filled pustules. The pus is a sign of the body’s immune response to infection.
- Risks: Pustular acne carries a high risk of scarring, so it’s crucial to avoid squeezing or popping the pustules, as this can worsen the condition.
Treatment:
- Inflammation Control: Similar to other types of inflammatory acne, focus on controlling inflammation with prescription medications.
- Early Intervention: Seek dermatological help early to prevent long-term scarring and manage pustular acne effectively.
Acne Scars
Acne scars develop when inflammation from acne extends deep into the skin, causing damage to the underlying tissue. This can result in visible marks even after the acne itself has healed. Scars can appear as redness, indentations (craters), or hyperpigmentation. Early and effective treatment of acne can help minimize the risk of developing scars.
Treatment:
- Targeted Approaches: Different types of scars require specific treatments:
- Crater Scars: Treatments like dermapen (microneedling) can help stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture.
- Redness: Photofacials (light therapy) can reduce redness and improve overall skin tone.
- Hyperpigmentation: Chemical peels and iontophoresis can help lighten dark spots and even out skin tone.
- Enhanced Effectiveness: Combining treatments such as chemical peels with iontophoresis can boost results and speed up scar improvement.
How To Get Rid Of Acne Scars Fast
Chemical Peeling Advantages And Disadvantages
Recurring Acne
Identification:
- Link to Health Issues: Recurring acne, especially when it appears in the same areas repeatedly, can be a sign of underlying health issues or lifestyle factors. This pattern may indicate hormonal imbalances, stress, or other health concerns.
- Spot Specificity: Acne that recurs in the same spot might suggest specific problems, such as hormonal fluctuations or persistent irritation in that area.
Treatment:
- Holistic Approach: To effectively address recurring acne, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This involves not just treating the skin but also making lifestyle adjustments such as improving diet, managing stress, and ensuring proper hydration.
- Consultation: Seeking advice from a dermatologist is crucial for diagnosing and treating the root causes of recurring acne. They can provide tailored recommendations and treatments to help prevent future breakouts.
Acne by Location

Forehead/Temples:
- Causes: Acne in this area can often be linked to residue from shampoos, conditioners, or hair products. Hair friction or the oils from your hair can also contribute. Additionally, hormonal imbalances might play a role.
- Prevention: Ensure you thoroughly rinse out hair products and avoid letting hair touch your face. Opt for non-comedogenic hair products.
Nose/T-Zone:
- Causes: This area is prone to acne due to higher sebum production and frequent clogging of pores, particularly common in oily skin types and teenagers.
- Prevention: Use oil-free, non-comedogenic skincare products and exfoliate regularly to keep pores clear.
Cheeks:
- Causes: Acne on the cheeks can be triggered by lifestyle factors, such as diet and stress, as well as hormonal imbalances. Contact with dirty hands or hair can also worsen the condition.
- Prevention: Maintain a clean face by avoiding touching it frequently, use a clean pillowcase, and adopt a balanced diet.
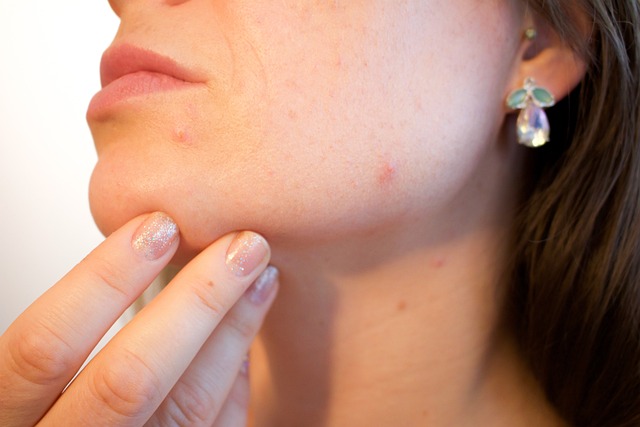
Chin/Jawline:
- Causes: Acne in this area is often linked to adult acne, which can be exacerbated by hormonal changes, stress, and poor lifestyle choices.
- Prevention: Manage stress, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and consider consulting a healthcare provider to address hormonal imbalances.
Back:
- Causes: Acne on the back is usually due to excessive sebum production, poor hygiene, or friction from clothing.
- Prevention: Wear breathable fabrics, practice good hygiene, and use body washes designed to combat acne.
Chest/Neck:
- Causes: Similar to facial acne, chest and neck acne is often caused by excess sebum and clogged pores.
- Prevention: Use gentle exfoliants and non-comedogenic products, and maintain good overall hygiene.
Acne by Type
Adult Acne:
- Characteristics: Commonly affects individuals over 20, especially in the U-zone (jawline and neck). It can be persistent and often results from a combination of stress, poor lifestyle choices, and inadequate skincare.
- Causes: Stress, hormonal changes, poor diet, and skincare habits contribute to its development. Sometimes linked to underlying health issues.
- Prevention: Adopt a consistent skincare routine, manage stress, and make healthy lifestyle choices. Consult a dermatologist if the condition persists.
Teen Acne:
- Characteristics: Typically affects the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin) during adolescence. This type is often more pronounced due to the hormonal changes of puberty.
- Causes: Increased sebum production and clogged pores caused by hormonal changes are common in teenagers.
- Prevention: Use oil-free, non-comedogenic products, maintain a balanced diet, and practice good hygiene. Regular cleansing and avoiding touching the face can help manage symptoms.
Female Acne:
- Characteristics: Often linked to hormonal fluctuations related to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Causes: Hormonal changes can lead to increased sebum production and acne outbreaks.
- Prevention: Track hormonal cycles, use appropriate skincare products, and consult a healthcare provider for hormonal treatments if necessary.
Male Acne:
- Characteristics: Common in males due to excess sebum production and can be exacerbated by inadequate skincare.
- Causes: Hormonal imbalances and poor skincare habits contribute to increased oiliness and acne.
- Prevention: Maintain a consistent skincare routine, use products designed for oily skin, and consider lifestyle changes to manage hormonal levels.












Post Comment