How To Treat Dark Spots On Face
Causes of Dark Spots
Hyperpigmentation
Dark spots, also known as hyperpigmentation, are caused by an overproduction of melanin in the skin. Melanin is the pigment that gives your skin its color. When your skin produces too much melanin, it can result in areas of darker skin. There are several reasons this might happen:
- Aging: As we get older, our skin can develop age spots or liver spots. These are usually small, flat, dark patches that appear on sun-exposed areas like the hands, face, and shoulders.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions such as melasma, often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy or the use of birth control pills, can cause dark patches, usually on the face.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun can increase melanin production, leading to sunspots or sun-induced hyperpigmentation. It’s why wearing sunscreen is so crucial!
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH occurs when the skin darkens following inflammation or injury. This can happen after:
- Acne: Acne scars can darken and become more noticeable as the skin heals, especially if the acne was severe or not treated properly.
- Insect Bites: Bites can cause inflammation and, as they heal, might leave behind dark marks.
- Burns: Any kind of burn, whether from heat or chemicals, can leave behind dark patches as the skin recovers.
- Incorrect Hair Removal: Using harsh methods like waxing or shaving can irritate the skin and lead to PIH if not done carefully.
Topical Treatments for Dark Spots

Ingredients for Dark Spot Treatment
When tackling dark spots, various topical treatments can help by targeting melanin production and improving skin turnover. Here’s a rundown of some effective ingredients:
- Kojic Acid: This ingredient works by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for melanin production, thereby helping to lighten dark spots. It’s commonly found in serums and creams. However, kojic acid can be irritating for sensitive skin, so it’s important to patch-test and use it cautiously.
- Retinoids: Retinoids, including retinol and tretinoin, boost cell turnover, which helps fade dark spots by shedding the top layers of skin and revealing fresher, less pigmented skin underneath. While effective, retinoids can be irritating and increase sun sensitivity, so they should be used at night and paired with sunscreen. They are not recommended during pregnancy.
- Chemical Exfoliants: Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid help with skin turnover and can improve the appearance of dark spots over time. These acids can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, so using them alongside a good sunscreen is crucial.
- Vitamin C: Known for its brightening properties, vitamin C helps to reduce pigmentation and even out skin tone. It also provides antioxidant protection against sun damage. It’s suitable for most skin types and can be used both morning and night.
- Azelaic Acid: Azelaic acid helps to reduce melanin production and can also improve skin texture, making it effective for treating both dark spots and acne. It’s generally well-tolerated and suitable for sensitive skin.
- Hydroquinone: This powerful ingredient reduces melanin production and can be highly effective for lightening dark spots. However, hydroquinone may cause irritation in some individuals and is banned in some countries due to potential risks associated with long-term use. It’s essential to use it under the guidance of a dermatologist and for short-term use only.
Cosmetic Procedures for Dark Spots
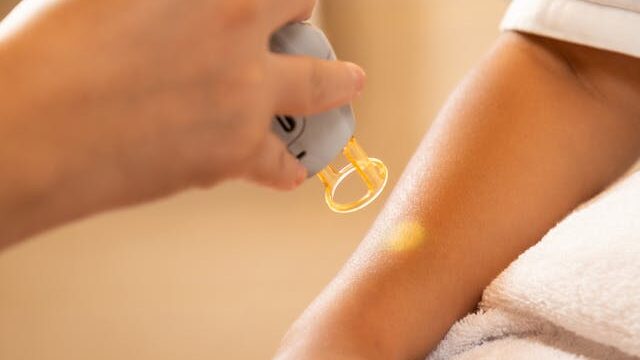
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a popular option for treating dark spots, as it targets pigmentation directly. Here’s how it works and what to consider:
- How It Works: Lasers use focused light to break down melanin and help fade dark spots. Different types of lasers can penetrate various depths of the skin, depending on the treatment needed.
- Considerations: While effective, laser therapy can sometimes exacerbate discoloration if not done correctly. It’s important to undergo a patch test before the full treatment to gauge your skin’s response. Recovery can vary, and it’s essential to follow post-procedure care instructions to minimize risks.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the outer layers and promote new skin growth:
- How It Works: Peels come in varying strengths, from superficial to deep, and work by exfoliating the top layers of skin. Stronger peels reach deeper layers, helping to reduce dark spots and improve overall skin texture.
- Considerations: Chemical peels can be more potent than over-the-counter exfoliants, which means they offer more dramatic results but also come with a longer recovery time. Expect some redness and peeling, and avoid sun exposure during the healing process to prevent further pigmentation issues.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a less invasive procedure that exfoliates the skin’s surface:
- How It Works: This technique involves using a device to gently buff away dead skin cells, helping to reduce the appearance of dark spots and improve skin texture.
- Considerations: Microdermabrasion has minimal recovery time and is generally suitable for those with lighter pigmentation issues. However, it may not be the best choice for individuals prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) or those with deep scarring, as it can sometimes aggravate these conditions.
Prevention and Care
To keep dark spots at bay and protect your skin, sunscreen is a must. It shields your skin from UV rays, which can worsen dark spots and lead to more damage. Regular check-ins with a dermatologist are also a great idea—they can help you find the best treatments and personalized care. Beyond products and treatments, the best prevention is to avoid skin damage in the first place. Protect your skin from the sun, avoid picking at blemishes, and be gentle with your skincare routine. Taking these steps can keep your skin looking even and healthy.













4 comments